Windows Syswow64 Powershell.exe Malware Errors
The presence of Windows Syswow64 Powershell.exe Malware Errors is causing problems for computer users, prompting concerns about the potential spread of the malicious software.
- Download and install the Exe and Dll File Repair Tool.
- The software will scan your system to identify issues with exe and dll files.
- The tool will then fix the identified issues, ensuring your system runs smoothly.
Understanding Windows SysWOW64 and Powershell.exe
Windows SysWOW64 is a folder that contains 32-bit operating system files on a 64-bit machine. Powershell.exe is a tool used to run scripts on a computer. Both of these aspects can be targets for malware attacks. Malware can infect the SysWOW64 folder and cause errors, while also using Powershell to carry out malicious tasks.
If you encounter malware errors, one solution is to run a scan using Windows Defender or another antivirus tool. You can also use System File Checker to check for corrupted files.
To fix any issues related to SysWOW64 and Powershell.exe, you can try running a script or using the Fix button in the tool you are using. The script may involve edits to work files or schedules tasks to keep your system clean.
Before taking any action items, make sure you are logged in as an Administrator and have a backup of your important documents. When running a script or tool, be patient and wait for the message on the screen before rebooting your PC. With these methods, you can address any malware errors related to SysWOW64 and Powershell.exe.
Is Powershell.exe Safe? How to Detect and Remove Viruses
Powershell.exe can be safe, but it can also be infected with viruses. If you’re experiencing errors with Windows Syswow64 Powershell.exe, there are steps you can take to detect and remove malware. First, run a virus scan on your machine using Windows Defender or another antivirus software. Check the malware analysis report to see if anything was found. Next, use System File Checker to scan for and repair any damaged or corrupted operating system files. Look for suspicious apps or files in the location where the error message appeared. Remove anything that looks suspicious. You can also use task scheduler to check for any scheduled tasks that could be causing the errors. Finally, run a scan on any external devices like USB-storage drives or CDs. Once you’ve cleaned up any viruses, reboot your PC and run another scan to make sure everything is clear. Be patient – it may take lots of time to complete all of these action items.
Latest Update: February 2026
We strongly recommend using this tool to resolve issues with your exe and dll files. This software not only identifies and fixes common exe and dll file errors but also protects your system from potential file corruption, malware attacks, and hardware failures. It optimizes your device for peak performance and prevents future issues:
- Download and Install the Exe and Dll File Repair Tool (Compatible with Windows 11/10, 8, 7, XP, Vista).
- Click Start Scan to identify the issues with exe and dll files.
- Click Repair All to fix all identified issues.
Common Errors Associated with Powershell.exe and How to Fix Them
- Uninstall and Reinstall PowerShell
- Open the Control Panel and select Programs and Features.

- Find Windows PowerShell and select Uninstall.
- Restart the computer.
- Download and install the latest version of PowerShell from the official Microsoft website.
- Restart the computer.
- Scan for Malware
- Open Windows Defender or another trusted antivirus program.
- Select Scan Options.
- Select Full Scan.
- Select Scan Now.

- Wait for the scan to complete.
- Remove any malware found.
- Restart the computer.
- Check for Corrupted System Files
- Open Command Prompt as an administrator.
- Type sfc /scannow and press Enter.
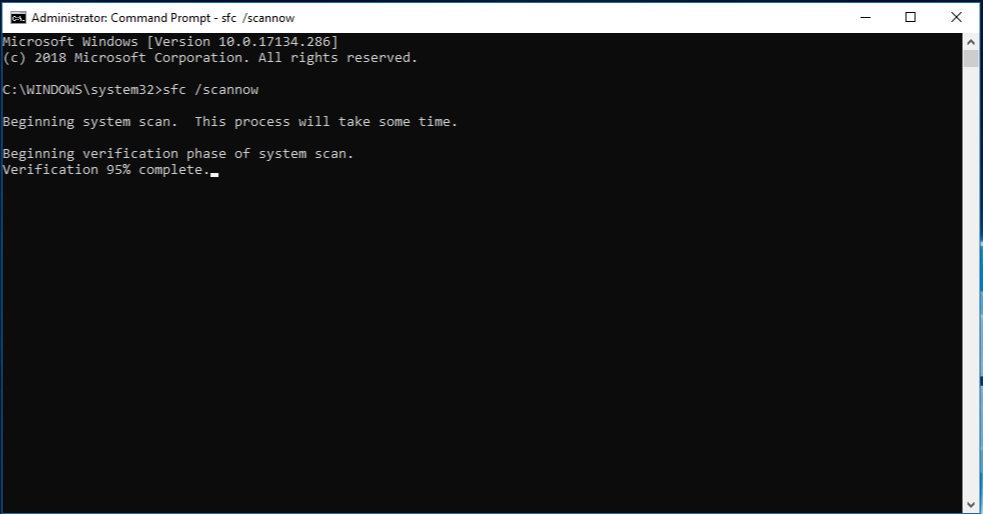
- Wait for the scan to complete.
- Restart the computer.
- Check for Windows Updates
- Open Settings and select Update & Security.
- Select Check for Updates.
- Install any available updates.
- Restart the computer.
- Check for Driver Updates
- Open Device Manager.
- Find the device that needs an update.
- Right-click on the device and select Update Driver.
- Choose the option to Search Automatically for Updated Driver Software.
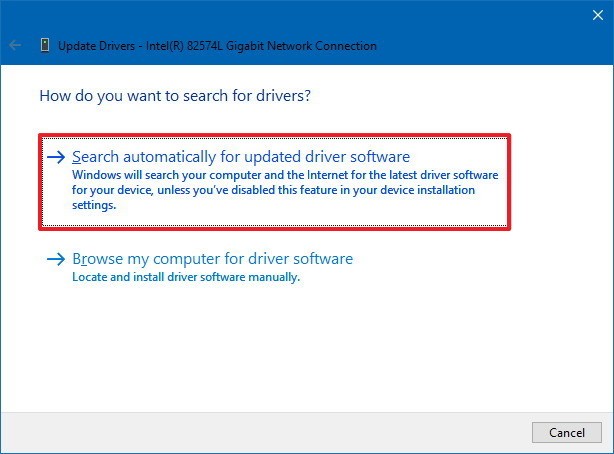
- Follow the prompts to install the driver update.
- Restart the computer.
Repairing or Removing Powershell.exe: Methods and Considerations
Repairing or removing Powershell.exe requires careful consideration of the issue at hand. First, users should determine if the Powershell.exe file is infected with malware by analyzing a malware report. If it is found to be infected, the file should be removed to prevent further damage.
To remove Powershell.exe, users can run a virus scan or use a malware removal tool. If repairing the file is necessary, users can try downloading a new Powershell.exe file from a trusted source or using a Windows task to replace the file.
When editing or cleaning up the file, users should make sure to backup their work-files and documents beforehand. It is also important to run checks and point to the correct location of the file.
For Windows 10 users, repairing or removing Powershell.exe can be done through the command prompt or by running a FIXLIST script. Users should follow the prompts on the screen and exercise patience when waiting for the fix button to appear.
Tips for Avoiding Powershell.exe Issues and Improving System Performance
| Tips for Avoiding Powershell.exe Issues and Improving System Performance |
|---|
| 1. Keep Your System Up-to-Date: Make sure your Windows operating system is up-to-date with the latest security patches and updates. This will help prevent malware attacks and keep your system running smoothly. |
| 2. Use Anti-Malware Software: Install and regularly update anti-malware software to protect your system from malware attacks. This will help detect and remove any malicious software that may be causing issues with Powershell.exe. |
| 3. Avoid Downloading Suspicious Files: Only download files from trusted sources and avoid downloading any suspicious files or attachments. Malware can often be disguised as legitimate files, so be cautious when downloading anything from the internet. |
| 4. Enable Windows Defender: Windows Defender is a built-in anti-malware program that can help protect your system from malware attacks. Make sure it is enabled and regularly updated to ensure maximum protection. |
| 5. Disable Unnecessary Services: Disabling unnecessary services can help improve system performance and reduce the risk of malware attacks. Services such as Remote Registry, Remote Desktop, and Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) should only be enabled if necessary. |
| 6. Use a Firewall: A firewall can help prevent unauthorized access to your system and protect against malware attacks. Make sure your firewall is enabled and configured correctly to maximize protection. |
| 7. Monitor Powershell.exe Activity: Monitor Powershell.exe activity to detect any suspicious activity or malware attacks. Powershell.exe is a legitimate Windows program, but it can be used by malware to execute malicious code. |


