Troubleshooting Microsoft Exchange RPC Client Access Service Errors
This article provides a concise overview of troubleshooting Microsoft Exchange RPC (Remote Procedure Call) Client Access Service errors. It aims to assist users in understanding the common issues and offering practical solutions to resolve them effectively.
- Download and install the Exe and Dll File Repair Tool.
- The software will scan your system to identify issues with exe and dll files.
- The tool will then fix the identified issues, ensuring your system runs smoothly.
Purpose of microsoft.exchange.rpcclientaccess.service.exe

The microsoft.exchange.rpcclientaccess.service.exe is a critical component of the Microsoft Exchange RPC Client Access Service. This service allows clients, such as Microsoft Outlook, to connect to and interact with the Exchange Server.
If you encounter errors related to this service, it can disrupt email communication and access to Exchange Server resources. Common issues include memory leaks, RPC failures, and service crashes.
To troubleshoot these errors, first check the event logs for any specific error messages related to the service. Additionally, ensure that the service is running and that there are no issues with the underlying hardware or software, such as the CPU or memory.
If you are unable to resolve the issue, you can search the Microsoft Knowledge Base for known issues and workarounds. It may also be helpful to seek support from Microsoft or consult with an IT professional familiar with Exchange Server troubleshooting.
Legitimacy of microsoft.exchange.rpcclientaccess.service.exe
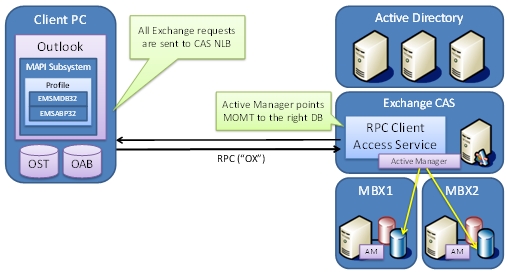
When encountering RPC Client Access Service errors, it is essential to ensure that the microsoft.exchange.rpcclientaccess.service.exe file is not corrupted or infected with malware. To do this, you can check the file’s location, checksum, and digital signature for authenticity.
Additionally, make sure that the necessary Windows components, such as MAPI and Active Directory, are properly configured and functioning. Keep an eye out for any issues with Microsoft Outlook, email archiving, or database connectivity.
If you suspect a memory leak or CPU time consumption, monitor the performance of the RPC Client Access Service using tools like Performance Monitor. You can also consult the Microsoft Knowledge Base for known issues and recommended workarounds.
Origin of microsoft.exchange.rpcclientaccess.service.exe

The microsoft.exchange.rpcclientaccess.service.exe is a critical component of Microsoft Exchange Server. It is responsible for handling remote procedure calls (RPC) made by client devices to access Exchange Server resources.
When troubleshooting errors related to this service, it is important to consider various factors such as the version of Windows and Exchange Server being used, the configuration of the Active Directory, and any recent software updates or service packs installed.
Common issues with the RPC Client Access Service include memory leaks, email archiving problems, and database corruption. To resolve these issues, it may be necessary to check the server’s CPU time, analyze feedback and logs, and implement specific algorithms or workarounds.
In some scenarios, it may be necessary to perform a rollup or reinstall the service to ensure proper functionality. It is always recommended to consult Microsoft’s official documentation and seek professional assistance if needed.
Usage of microsoft.exchange.rpcclientaccess.service.exe
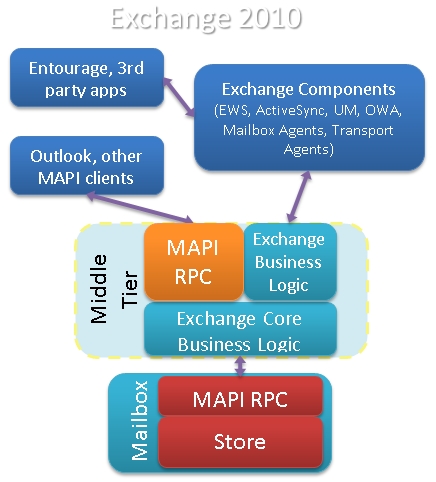
The microsoft.exchange.rpcclientaccess.service.exe is a crucial component of Microsoft Exchange Server that handles the client access to the server through the Remote Procedure Call (RPC) protocol. However, errors with this service can lead to issues in accessing and managing Exchange data.
To troubleshoot Microsoft Exchange RPC Client Access Service errors, follow these steps:
1. Check for any recent changes or updates that might have caused the issue.
2. Restart the RPC Client Access Service to resolve temporary glitches.
3. Verify the server’s system requirements, such as Windows XP Service Pack level and memory allocation.
4. Monitor the event logs for any error messages or patterns that could indicate the root cause.
5. Consider applying the latest service packs and rollup updates for Microsoft Exchange Server.
6. If the issue persists, try disabling any third-party applications or services that might be conflicting with RPC Client Access Service.
7. Consult Microsoft’s official support documentation or seek assistance from their technical support team for further troubleshooting steps.
Associated software with microsoft.exchange.rpcclientaccess.service.exe

- Microsoft Exchange Server: The main software that utilizes the microsoft.exchange.rpcclientaccess.service.exe file is Microsoft Exchange Server. This software is used for email, calendar, and contact management in a corporate environment.
- Active Directory: Active Directory is a directory service used by Microsoft Exchange Server to store and manage information about network resources, including user accounts, groups, and permissions.
- Microsoft Outlook: Microsoft Outlook is the client application commonly used to access Microsoft Exchange Server. It provides features like email, calendar, and contacts, and relies on the RPC Client Access Service for communication with the server.
- Windows Server: The RPC Client Access Service is typically run on a Windows Server operating system, which provides the underlying infrastructure for Microsoft Exchange Server.
- Client Access Server (CAS): The Client Access Server is a role in Microsoft Exchange Server that handles client connections, including the RPC Client Access Service. It acts as a gateway between the clients and the Exchange server.
Creator of microsoft.exchange.rpcclientaccess.service.exe

If you’re experiencing errors with the Microsoft Exchange RPC Client Access Service, there are a few troubleshooting steps you can take to resolve the issue.
First, check for any recent updates or service pack installations that may have caused the problem. Make sure that your server and client are both running the same version of Exchange.
Next, verify that the RPC Client Access Service is running on the server. You can do this by opening the Services console and looking for the Microsoft Exchange RPC Client Access Service. If it’s not running, start it and see if that resolves the issue.
If the service is running but you’re still experiencing errors, it could be due to a memory leak. In this case, it may be helpful to restart the server to clear out any lingering memory issues.
System file status of microsoft.exchange.rpcclientaccess.service.exe
![]()
1. Open the Command Prompt as an administrator.
2. Type “sfc /scannow” and press Enter. This will initiate a system file scan and repair any corrupted files.
3. Wait for the scan to complete and follow the on-screen instructions if any issues are found.
4. Restart your computer and check if the RPC Client Access Service errors have been resolved.
By verifying the system file status and running a scan, you can effectively troubleshoot Microsoft Exchange RPC Client Access Service errors. If the issue persists, it is recommended to seek further assistance from a professional or refer to Microsoft’s official documentation for additional support.
Malware potential of microsoft.exchange.rpcclientaccess.service.exe
The microsoft.exchange.rpcclientaccess.service.exe is a critical component of Microsoft Exchange RPC Client Access Service. However, it has the potential to be exploited by malware. To troubleshoot errors related to this service, it is important to be aware of the malware risks associated with it.
One way to mitigate the risk is to ensure that your system is up to date with the latest Windows XP patches and updates. Additionally, it is crucial to have reliable antivirus software installed and regularly updated to detect and remove any potential malware.
To further protect your system, it is recommended to implement security measures such as firewalls and access controls. Regularly monitoring and reviewing server logs can also help identify any suspicious activities.
In case of any errors or issues, it is advisable to seek assistance from Microsoft’s official support channels or consult online forums for troubleshooting tips and workarounds.
High CPU usage caused by microsoft.exchange.rpcclientaccess.service.exe
First, check for any recent updates or patches that may have caused compatibility issues. Make sure you have the latest version installed.
Next, try restarting the Microsoft Exchange RPC Client Access Service. This can often resolve temporary issues that may be causing high CPU usage.
If the problem persists, you can try disabling any unnecessary services or applications that may be conflicting with the RPC Client Access Service. Use the Task Manager to identify any processes that are using a high amount of CPU resources and end them if possible.
If none of these steps resolve the issue, it may be helpful to reach out to Microsoft support for further assistance. They can provide more specific guidance based on your specific scenario.
Troubleshooting microsoft.exchange.rpcclientaccess.service.exe issues
![]()
- RPC Client Access Service: Understanding the purpose and functionality of the Microsoft Exchange RPC Client Access Service.
- Common RPC Client Access Service issues and error messages encountered by users.
- Determining the root cause of RPC Client Access Service errors.
- Checking the server and client configuration settings for any misconfigurations.
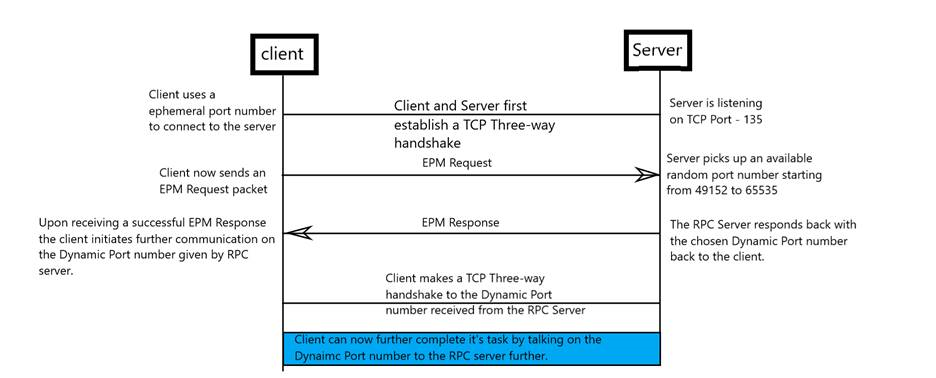
- Verifying the network connectivity between the server and the clients.
- Examining the Exchange server logs for any relevant error messages.
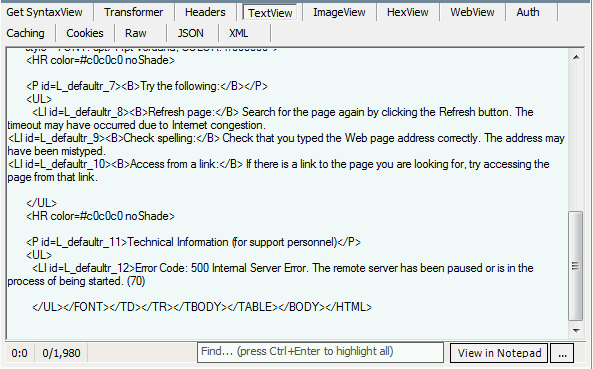
- Reviewing the Event Viewer for any related events or warnings.
- Ensuring that the Windows Firewall or any third-party firewalls are not blocking the RPC communication.
- Validating the RPC encryption settings to ensure they match between the server and the clients.
- Performing a server reboot to resolve any temporary issues.
- Recreating the Outlook profile to fix any profile corruption.
- Updating or reinstalling the Microsoft Exchange RPC Client Access Service if necessary.
- Consulting the Microsoft Exchange community or support forums for additional assistance.
Latest Update: July 2025
We strongly recommend using this tool to resolve issues with your exe and dll files. This software not only identifies and fixes common exe and dll file errors but also protects your system from potential file corruption, malware attacks, and hardware failures. It optimizes your device for peak performance and prevents future issues:
- Download and Install the Exe and Dll File Repair Tool (Compatible with Windows 11/10, 8, 7, XP, Vista).
- Click Start Scan to identify the issues with exe and dll files.
- Click Repair All to fix all identified issues.
Safe to end task or terminate microsoft.exchange.rpcclientaccess.service.exe?
If you encounter errors with the Microsoft Exchange RPC Client Access Service, you may wonder if it is safe to end the task or terminate the process “microsoft.exchange.rpcclientaccess.service.exe.”
In most cases, it is not recommended to end the task or terminate the process manually. This service is responsible for handling client connections to the Exchange Server and terminating it abruptly can cause disruptions in communication and potentially lead to data loss.
Instead, try the following troubleshooting steps:
1. Check the event logs for any related errors or warnings.
2. Restart the Microsoft Exchange RPC Client Access Service using the Services console.
3. Ensure that the Exchange Server and all related services are up to date.
4. Verify the MAPI connection settings between the client and the server.
5. Run the Exchange Best Practices Analyzer to identify any configuration issues.
6. If the issue persists, consider contacting Microsoft Support for further assistance.
Always make sure to back up your data before making any changes, and if you are unsure, seek professional assistance.
Description of microsoft.exchange.rpcclientaccess.service.exe process
The microsoft.exchange.rpcclientaccess.service.exe process is a critical component of Microsoft Exchange Server. It is responsible for handling client requests and managing the communication between clients and the Exchange server.
If you encounter errors related to the RPC (Remote Procedure Call) Client Access Service, it can cause disruptions in client connectivity and access to Exchange resources.
To troubleshoot these errors, you can start by checking the event logs for any related error messages. Analyzing these messages can provide valuable information about the root cause of the issue.
Additionally, you can try restarting the RPC Client Access Service and verifying the configuration settings. Ensuring that the necessary ports are open and that the server’s network connectivity is stable is also important.
If the issue persists, you may need to explore more advanced troubleshooting techniques or seek assistance from Microsoft support.
Difficulty in deleting microsoft.exchange.rpcclientaccess.service.exe
![]()
If you are encountering difficulty in deleting the microsoft.exchange.rpcclientaccess.service.exe file, there are a few troubleshooting steps you can take. First, make sure that you have the necessary permissions to delete the file. You may need to login as an administrator or contact your IT department for assistance.
If you are still unable to delete the file, try stopping the RPC Client Access service before attempting to delete it. Open the Services app from the Start menu, locate the RPC Client Access service, right-click on it, and select “Stop”. Once the service has stopped, you should be able to delete the file.
If you are still having issues, it may be helpful to restart your server or perform a system reboot. This can help resolve any underlying issues that may be preventing the file from being deleted.
Running in the background: impact and implications
Running in the background, the Microsoft Exchange RPC Client Access Service plays a crucial role in facilitating communication between clients and the Exchange server. However, errors can occur, impacting the service’s functionality. These errors can have various implications, including disruptions in email access and synchronization. To troubleshoot these issues, follow these steps:
1. Check the server’s health and ensure all necessary services are running.
2. Verify the directory and permissions settings for the RPC Client Access Service.
3. Consider any recent changes or updates that may have affected the service.
4. Test ActiveSync connectivity to rule out client-related problems.
5. Monitor CPU and memory usage to identify potential resource constraints.
6. Seek feedback from users experiencing issues to gather additional information.
7. Review and apply any available patches or updates that address known issues.
8. Consider implementing workarounds if necessary to ensure uninterrupted service.
9. Analyze any specific scenarios or error messages encountered for further troubleshooting.
Not responding issues with microsoft.exchange.rpcclientaccess.service.exe
If you’re experiencing issues with the microsoft.exchange.rpcclientaccess.service.exe, there are a few troubleshooting steps you can try. Firstly, check if the service is running on the server. If not, start it manually. Secondly, verify that all necessary dependencies, such as the Microsoft Exchange ActiveSync service, are running. If any are not, start them as well.
If the issue persists, try restarting the server or running a repair on the Microsoft Exchange installation. It may also be helpful to check for any recent updates or patches that could be causing conflicts.
If none of these steps resolve the problem, you can try using a workaround by configuring a different client to access the Exchange server. This could involve using a different protocol or client software.
Keep in mind that these troubleshooting steps may vary depending on your specific scenario, so it’s always a good idea to consult Microsoft documentation or seek assistance from their support team.
Removal tools for microsoft.exchange.rpcclientaccess.service.exe
- Step 1: Open Task Manager by pressing Ctrl+Shift+Esc
- Step 2: Locate the microsoft.exchange.rpcclientaccess.service.exe process in the Processes tab
- Step 3: Right-click on the process and select End Task to terminate it
- Step 4: If the process cannot be terminated, go to the Details tab
- Step 5: Find the microsoft.exchange.rpcclientaccess.service.exe process in the list
- Step 6: Right-click on it and choose End Process Tree to forcefully terminate it and its child processes
- Step 7: Once the process is terminated, open File Explorer
- Step 8: Navigate to the directory where microsoft.exchange.rpcclientaccess.service.exe is located
- Step 9: Right-click on the file and select Delete to remove it
Startup behavior of microsoft.exchange.rpcclientaccess.service.exe
1. Check the server’s event logs for any related error messages or warnings. These logs can provide valuable information about the issue.
2. Verify the directory and client configurations to ensure they are set up correctly. Pay attention to any recent changes or updates that may have caused the problem.
3. Restart the service to see if that resolves the issue. Sometimes, a simple restart can fix temporary glitches.
4. Update the server’s firmware and drivers to the latest versions. This can address any compatibility issues and improve overall performance.
5. Consider using a workaround if the issue persists. This could involve modifying settings, implementing a different algorithm, or utilizing alternative services.
Performance impact of microsoft.exchange.rpcclientaccess.service.exe
When encountering performance issues, it is recommended to start by monitoring the server’s resources such as CPU and memory usage. High CPU usage can indicate heavy client activity or underlying issues with the server.
To optimize performance, ensure that the server has enough resources to handle client requests efficiently. Consider upgrading the server hardware or adding additional servers to distribute the workload.
Additionally, it is important to regularly monitor and maintain the Exchange server’s directory. This includes cleaning up old or unused mailboxes and optimizing the server’s algorithms for efficient processing.
By proactively managing the performance impact of microsoft.exchange.rpcclientaccess.service.exe, you can ensure a smooth and error-free operation of the Microsoft Exchange RPC Client Access service.
Updates for microsoft.exchange.rpcclientaccess.service.exe
- Explaining the purpose and role of microsoft.exchange.rpcclientaccess.service.exe.
- Common Error Messages: Listing the most frequent error messages encountered with the RPC Client Access Service.
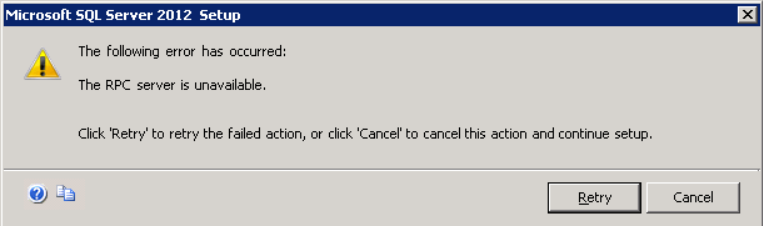
- Possible Causes: Describing the potential reasons behind the occurrence of these errors.
- Troubleshooting Steps: Providing a step-by-step guide to diagnose and resolve RPC Client Access Service errors.
- Updating microsoft.exchange.rpcclientaccess.service.exe: Highlighting the significance of keeping the RPC Client Access Service up to date.
- Recommended Solutions: Suggesting effective solutions to common RPC Client Access Service errors.
- Best Practices: Offering tips and best practices to optimize the performance and stability of the RPC Client Access Service.
- Conclusion: Summarizing the importance of addressing and resolving RPC Client Access Service errors promptly.
Download options for microsoft.exchange.rpcclientaccess.service.exe
- Download the latest version of microsoft.exchange.rpcclientaccess.service.exe from the official Microsoft website.
- Ensure that you have a valid Microsoft Exchange Server license before downloading and installing the RPC Client Access Service.
- Check for any available updates or service packs for your current version of Microsoft Exchange Server.
- Verify system requirements and compatibility with your operating system version before downloading the RPC Client Access Service.
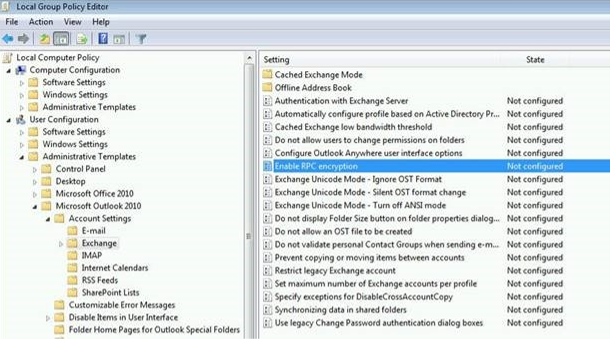
- If you are experiencing specific errors or issues, search for hotfixes or patches related to the problem and download them if available.
- Consider consulting Microsoft Support or their online community forums for further assistance with RPC Client Access Service errors.
Compatibility with different Windows versions

To determine compatibility, refer to Microsoft’s documentation which provides a compatibility matrix detailing the supported Windows versions for each Exchange version. Make sure to cross-reference the server’s Windows version with the Exchange version being used.
If the Windows version is not compatible, consider upgrading or downgrading the Windows version accordingly. This may involve reinstalling the operating system or performing an in-place upgrade.
It is also important to note that compatibility between the server and client machines is essential. Ensure that the client machines are running a compatible version of Windows and have the necessary updates installed.
By ensuring compatibility between Windows versions, you can reduce the likelihood of encountering RPC Client Access Service errors and ensure smooth operation of your Microsoft Exchange environment.
Alternatives to microsoft.exchange.rpcclientaccess.service.exe
1. Use the Exchange Management Shell: The Exchange Management Shell is a powerful command-line interface that allows you to manage and troubleshoot your Exchange environment. It provides similar functionality to the RPC Client Access Service, making it a viable alternative for troubleshooting errors.
2. Utilize Exchange Server Management Tools: Exchange Server Management Tools offer a graphical user interface (GUI) for managing Exchange Server. These tools provide an intuitive way to troubleshoot RPC Client Access Service errors and can be used as an alternative to the command-line approach.
3. Consider third-party monitoring and troubleshooting tools: There are various third-party tools available that specialize in monitoring and troubleshooting Exchange Server. These tools can provide comprehensive insights into RPC Client Access Service errors and offer advanced features for resolving them.
4. Consult Microsoft Support: If you are experiencing persistent RPC Client Access Service errors, it may be beneficial to reach out to Microsoft Support. Their experts can provide guidance specific to your environment and help you troubleshoot and resolve any issues you are facing.


